
In the automotive industry, selecting the right adhesive tape can significantly impact product integrity, efficiency, and long-term durability. Among the most widely used adhesive solutions are transfer tapes and double-sided foam tapes. Both offer unique properties, but their suitability often depends on specific automotive applications, such as attaching emblems, bonding trims, or mounting sensors.
This article breaks down the key features, differences, performance factors, and use cases of each tape type, helping engineers, procurement teams, and manufacturers make informed decisions.
Adhesive tapes have become essential in modern automotive manufacturing, replacing traditional mechanical fasteners for many lightweight and seamless applications. Common uses include:
These applications demand adhesives that are durable, weather-resistant, and capable of withstanding temperature extremes. The right choice of tape can contribute to better aesthetics, reduced weight, improved fuel efficiency, and faster assembly processes.
Transfer tapes are pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSA) that come without a carrier or foam core. They are made entirely of adhesive, coated on a release liner. When applied, the liner is peeled off, leaving behind only the adhesive layer bonded to the surface.
Transfer tapes are commonly used where minimal thickness is desired, such as in bonding decorative trims, lightweight components, or nameplates that require a clean and nearly invisible bond line.
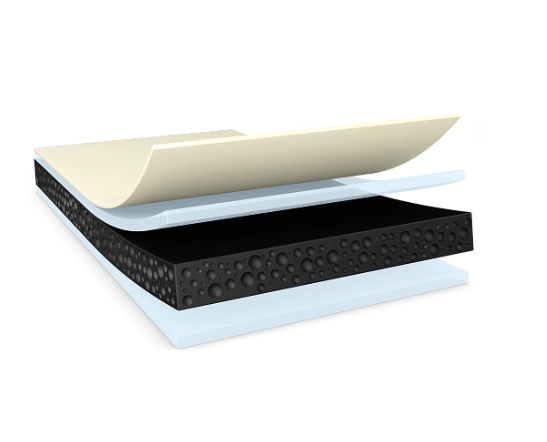
Double-sided foam tapes consist of a foam core (typically polyethylene, polyurethane, or acrylic foam) with adhesive on both sides. The foam adds thickness and flexibility, enabling it to conform to irregular or textured surfaces.
Foam tapes are widely used in bonding applications where surface irregularity and dynamic loads are expected, such as in the assembly of mirrors, panels, or vibration-sensitive components.
| Feature | Transfer Tapes | Double-Sided Foam Tapes |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Pure adhesive with liner | Foam core with adhesive layers |
| Thickness | Very thin (<0.1mm) | Ranges from 0.5mm to several mm |
| Flexibility | Highly conformable | Excellent for gap filling |
| Vibration Dampening | Minimal | Excellent |
| Surface Adaptability | Best for smooth surfaces | Ideal for textured/uneven areas |
| Aesthetic Finish | Nearly invisible bond line | May be slightly visible |
Transfer tapes provide strong initial tack and reliable long-term adhesion, especially when bonding to high surface energy materials like metals and glass. However, foam tapes typically offer higher peel and shear strength, making them more suited for load-bearing applications and where strong joint integrity is required over time.
Both tapes can be formulated for high-temperature environments, but acrylic-based foam tapes often offer better resistance to extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and humidity, making them more reliable in exterior or under-the-hood applications.
Transfer tapes work well on flat, smooth surfaces. In contrast, foam tapes perform better on irregular, contoured, or rough surfaces, as the foam helps bridge gaps and improve contact area for bonding.
One of the significant advantages of foam tapes is their shock and vibration dampening ability. This makes them ideal for mounting components that experience movement or require noise isolation, such as dashboard panels or electric modules.
The choice between transfer tapes and foam tapes should depend on application-specific requirements, including substrate type, load expectations, and environmental exposure.
When it comes to automotive applications, both transfer tapes and double-sided foam tapes serve vital roles. The decision is not about which tape is universally better, but rather which performs better based on the intended use case.
Transfer tapes offer a clean, strong solution for light-duty bonding on smooth surfaces. On the other hand, double-sided foam tapes bring versatility, gap-filling ability, and vibration resistance for more complex or heavy-duty automotive needs.
Understanding the structural, environmental, and performance requirements of each component can help automotive engineers and manufacturers select the most suitable adhesive solution—ensuring durability, performance, and customer satisfaction.